INTRODUCTION
The Microsoft Windows Update client program requires Microsoft Windows HTTP Services (WinHTTP) to scan for available updates. Additionally, the Windows Update client uses the Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) or Delivery Optimization (DO) to download these updates. Microsoft Windows HTTP Services, BITS and DO run independently of Microsoft Internet Explorer. Both these services must be able to detect the proxy server or proxy servers that are available in your particular environment. This article describes the various proxy server detection methods that are available. Additionally, this article describes the situations where Windows Update uses a particular proxy server detection method.
Additional Information
The Automatic Updates service is configured to download and install updates from the Microsoft Windows Update website
The Automatic Updates service can automatically download and install updates from the Windows Update website. The Automatic Updates service does not require user interaction because this service runs in the context of the Local System account. WinHTTP has been employed, instead of WinINet in Internet Explorer, as the Automatic Updates service affects system-wide level configuration and should require administrator level control. WinHTTP is considered as more appropriate in this type of usage scenario. The Automatic Updates service can only discover a proxy server by using one of the following methods:
-
The proxy server is manually configured by using the Netsh command.
-
Web Proxy Auto Detect (WPAD) settings are configured in either of the following locations in the network environment:
-
The Domain Name System (DNS) options
-
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) options
-
For Windows Update scan URLs which are used for update detection (SimpleAuth Web Service, Client Web Service):
-
The system proxy is attempted (WinHTTP).
-
If the Windows Update Agent (WUA) fails to reach the service due to certain proxy, service, or authentication error codes, then the user proxy is attempted. (Generally it is the signed-in user IE settings or WinINet.)
-
For intranet WSUS update service URLs, we provide an option to choose the proxy behavior: GPS: Specify intranet Microsoft update service location
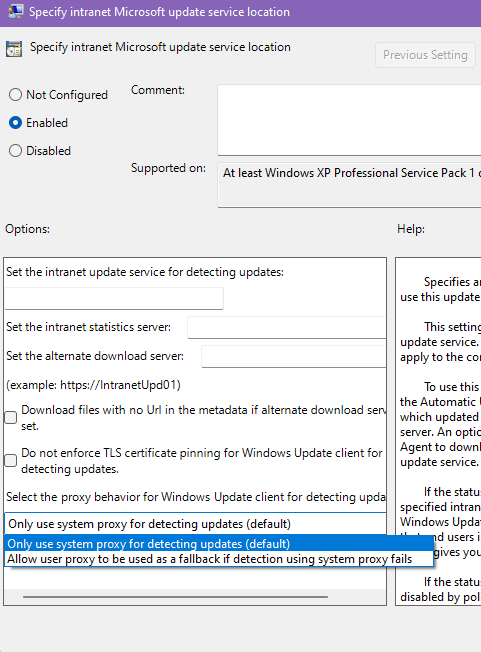
-
For Windows Update URLs which are NOT used for update detection (e.g., URLs used for downloads or reporting):
-
The user proxy is attempted.
-
If the Windows Update Agent (WUA) fails to reach the service due to certain proxy, service, or authentication error codes, then the system proxy is attempted.
A description of the Web Proxy Auto Detect (WPAD) feature
The WPAD feature lets services locate an available proxy server by querying a DHCP option or by locating a particular DNS record.
A description of the Netsh.exe tool
The Netsh.exe tool is used to configure a system-wide static proxy. You can use commands in the netsh winhttp context to configure proxy and tracing settings for Windows HTTP. The Netsh commands for winhttp can be run manually at the netsh prompt or in scripts and batch files. The Netsh.exe tool is useful if you cannot implement WPAD.
To configure a proxy server by using the Netsh.exe tool
To use the Netsh.exe tool to configure a proxy server, follow these steps:
-
Click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
-
At the command prompt, type netsh winhttp set proxy proxyservername:portnumber, and then press ENTER. In this command, replace proxyservername with the fully qualified domain name of the proxy server. Replace portnumber with the port number for which you want to configure the proxy server. For example, replace proxyservername:portnumber with proxy.domain.example.com:80.
To remove a proxy server by using the Netsh.exe tool
To use the Netsh.exe tool to remove a proxy server and to configure "direct access" to the Internet, follow these steps:
-
Click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
-
At the command prompt, type netsh winhttp reset proxy, and then press ENTER.
To verify the current proxy configuration by using the Netsh.exe tool
To use the Netsh.exe tool to verify the current proxy configuration, follow these steps:
-
Click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
-
At the command prompt, type netsh winhttp show proxy, and then press ENTER.
Supported .pac files
For more information about the supported types of .pac files, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
https://docs.microsoft.com/windows/win32/winhttp/winhttp-autoproxy-support










