INTRODUCTION
Microsoft has released a Microsoft security advisory about this issue for IT professionals. The security advisory contains additional security-related information. To view the security advisory, go to the following Microsoft website:
Resolution
To get the stand-alone package for this update, go to the Microsoft Update Catalog website.
More Information
1: Purpose of this security update
The security update strengthens how the identity of remote IPsec servers is validated if there is a remote connection from an IPsec client. The installation of this update is a three-step process. The process is outlined in this section and is documented in detail in this article.
To install this update, follow these steps:
-
Install the update on the client system that improves remote server validation. The update remains disabled after installation until the administrator follows step 2 and manually enables the update. (This is described in section 4.1.) If there is a client-to-gateway configuration, the update should be installed on the client computer. If there is a site-to-site configuration, both communication remote servers should receive the installation.
-
Update the certificate on the server whose identity has to be validated according to the new validation rules. (This is described in the "Deployment instructions" section.)
-
Update the registry on the validation computers to include the new validation rules. As soon as these rules are set in the registry, the update automatically starts enforcing the new rules while it establishes a tunnel with the remote party.
Note This update is applicable only for tunnel-mode connections. Transport-mode connections are not affected.
2: Who should install this security update?
Enterprise administrators who have the following configurations should consider updating their remote client and servers for improved security:
-
DirectAccess with certificate-based AuthIP
In this configuration, the update has to be installed on Windows 7-based client computers. The server whose certificate has to be updated in the configuration can be running Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, or Windows Server 2012 R2.
This update will not have any effect if it is installed on a Windows 8 certificate-based deployment. -
DirectAccess with KerbProxy authentication AuthIP
In this configuration, the update has to be installed on Windows 8-based or Windows 8.1-based client computers. No changes are required on the server. -
IPsec with certificate-based authentication
This is the most versatile configuration. It may be configured as client-to-gateway or as site-to-site.
|
Scenario |
Protocol |
Authentication method |
Installation type |
Platforms to be patched |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IPsec |
IKEv1 |
Certificate based |
Site-to-site (for example, RRAS) |
Win 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|
Client-to-server |
Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7 |
|||
|
DirectAccess |
AuthIP |
Certificate based |
Client-to-server (For example, DirectAccess) |
Windows 7 |
|
KerbProxy |
Client-to-server (For example, DirectAccess) |
Windows 8, Windows 8.1 |
Important note: For certificate-based authentication (IPsec or DirectAccess):
-
Site-to-site: Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 don’t have to be patched because the in-box certificate checks are sufficient.
-
Client to Gateway: Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 don’t have to be patched because the in-box certificate checks are sufficient.
For more information about how to configure certificate checks in Windows 8, 8.1, Server 2012, and Server 2012 R2, see the following Microsoft TechNet article:
3: Deployment scenarios
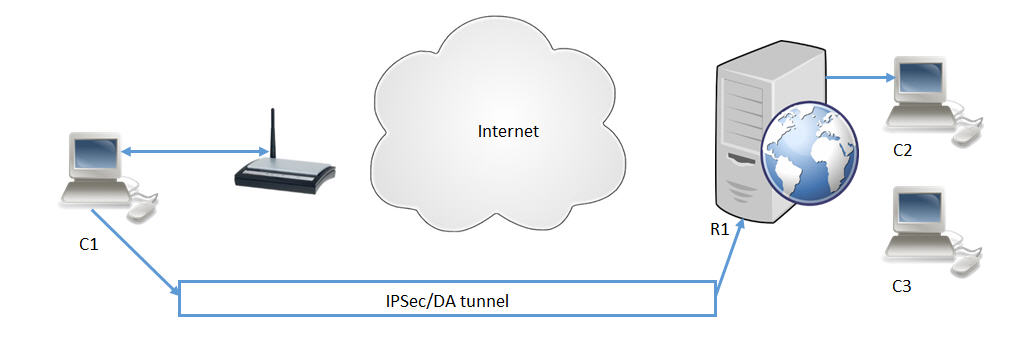
3.1: IPsec client to gateway
A typical client-to-gateway configuration is depicted in this section. The update will improve the check that computer C1 does on the validity of server R1.
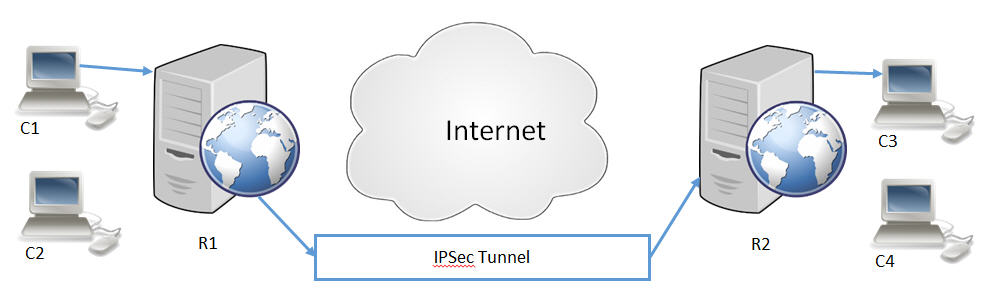
3.2: IPsec site to site
A common traffic-triggered IPsec site-to-site tunnel is depicted here. Server R1 and server R2 will have to have this update and its related configuration in order to enforce more rigorous checks on other servers’ validity.
4: Deployment instructions
4.1: Description of the security update
As part of security update 2862152, IPsec enforces more checks in IPsec negotiation in certificate authentication methods (for Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003) and KerbProxy authentication (for Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012). During IPsec negotiation, IPsec also checks the listed attributes against the registry-configured values as follows:
Windows 7 and earlier operating systems
-
If only the IP address and the EKU are configured, IPsec checks for destination IP address and EKU object identifier (also known as OID).
-
If only the IP address and DNS are configured, IPsec checks for destination IP address and DNS (certificate) name.
-
If the IP address, DNS, and EKU are configured, IPsec checks for destination IP address and EKU object identifier.
Notes
-
DNS (certificate) s the certificate name on the server (or responder side).
-
EKU object identifier is the Extended Key Usage identifier that is in the server certificate.
Windows 8 and Windows 8.1
-
Destination IP address and SPN values
The service principal name (SPN) is generally in the following format:host/<ComputerName>.<ComputerDomain>.comAdministrators must provide the valid IP, DNS names/EKU object identifiers (in Windows 7 or earlier operating systems), or valid IP address and SPN values (in Windows 8 and later versions) through registry settings. Each keying module will have a separate registry that will have a subkey for each authentication method.
The same settings can also be configured on the responder computer to help secure the responder. This is applicable only for Windows 7 and earlier versions.
In Windows 8 and later versions, only the initiator computer can be configured. The responder cannot be configured.
4.2: Certificate deployment - Windows 7 and earlier versions
4.2.1 IPsec scenario
4.2.1.1 EKU configuration on the client:
-
If your IPsec client already has a certificate that has an EKU, you do not have to update or redeploy a new certificate on the IPsec client system. On the IPsec server, a new certificate with the EKU is set to be deployed.
Note This certificate has to be chained to the same root certification authority (CA) that was configured in the IPsec policy. Configure this new EKU in the client's registry settings. -
Certificates that do not have an EKU are considered as "all-purpose certificates." When such certificates are used with this update, the new EKU checks will not be enforced. If you still want to enforce checks against a certificate, configure only DNS settings.
4.2.1.2 DNS configuration on the client:
-
If you want to use DNS-based validations, you can configure the DNS name (certificate name) of the server certificate in the client's registry settings.
Note If EKU is configured, DNS settings will not be considered. Therefore, if you want to use DNS-based validations, configure only DNS settings.
4.2.2 Site-to-site scenario
4.2.2.1 EKU configuration:
-
If your initiator or responder already has a certificate that has an EKU, you do not have to update or redeploy any certificate on the initiator or responder. Just configure the peer certificate's EKU in the registry settings on both ends.
-
If your initiator or responder certificate has no EKU, this means that it is an "all-purpose certificate" and that the new EKU checks will not be enforced. If you still want to enforce checks against a certificate, configure only DNS settings.
4.2.2.2 DNS configuration:
-
If you want to use DNS-based validations, you can configure the DNS name (certificate name) of the peer certificate in the registry on both sides.
Note If EKU is configured, DNS settings will not be considered. Therefore, if you want to use DNS-based validations, configure only DNS settings.
4.3: Registry settings in Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008
The validations will be enabled only when the registry keys are configured.
Note The validation will be forced even if the registry key has no value or data.
-
4.3.1: Certification authentication by using AuthIP
-
Registry key: HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\IKEEXT\Parameters\IPsecTunnelConfig\AuthIP\Cert
-
Registry name: This can be any name (for example, Tunnel1).
-
Type: REG_MULTI_SZ
-
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address> <DNS1> <DNS2> <DNS3> <custom EKU OID>
Data separators can be "space" or "tab" or "new line." For example, the data can also be configured as follows:
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address><DNS1>
<DNS2>
<DNS3>
<custom EKU OID>
The custom EKU OID should be configured by using the "EKU:" prefix format as shown in the following:EKU:<EKU OID>
The registry can have more than one registry name:-
Registry name: This can be any name (for example, Tunnel2).
-
Type: REG_MULTI_SZ
-
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address> <DNS4> <DNS5> <DNS6> <custom EKU OID>
-
-
4.3.2: Certification authentication by using IKEv1
-
Registry key: HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\IKEEXT\Parameters\IPsecTunnelConfig\IKEV1\Cert
-
Registry name: This can be any name (for example, Tunnel1).
-
Type: REG_MULTI_SZ
-
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address> <DNS1> <DNS2> <DNS3> <custom EKU OID>
Data separators can be "space" or "tab" or "new line." For example, the data can also be configured as follows:
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address><DNS1>
<DNS2>
<DNS3>
<custom EKU OID>
The custom EKU OID should be configured by using the "EKU:" prefix format as shown in the following:EKU:<EKU OID>
The registry can have more than one registry name:-
Registry Name: This can be any name (for example, Tunnel2).
-
Type: REG_MULTI_SZ
-
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address> <DNS4> <DNS5> <DNS6> <custom EKU OID>
Each entry can have no more than 10 DNS names and only one custom EKU specified.
The maximum number of DNS names configured per entry is 10.
Note If the size of the entry exceeds 16,384 characters, that entry will be ignored. This includes the IP address size and EKU size.
Only one EKU can be considered per tunnel destination (for example, per IP). The search is iterative. If there are more than one "IP" entries configured, the first configured EKU for that IP address entry will be considered for validation.
The maximum number of tunnels that can be configured under the registry path is 1,024.
Notes-
"IP" values must be configured. Administrators can configure either DNS or EKU based on their needs.
-
If only EKU is configured, we validate the EKU that is present in the peer certificate and enable or disallow authentication based on the validation result.
-
If only DNS name is configured, we validate only the subjectAltName present in the certificate and enable or disallow authentication based on the validation result.
-
If EKU and DNS are configured, we validate only EKU and enable or disallow authentication based on the validation.
-
DNS approach:
-
You can specify any string in the Name field.
-
If your server has an IPv6 address, you can specify the same IPv6 address instead of the IPv4 address.
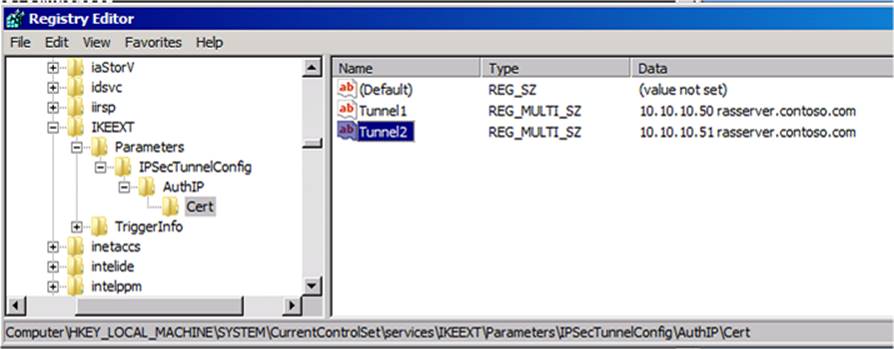
EKU approach: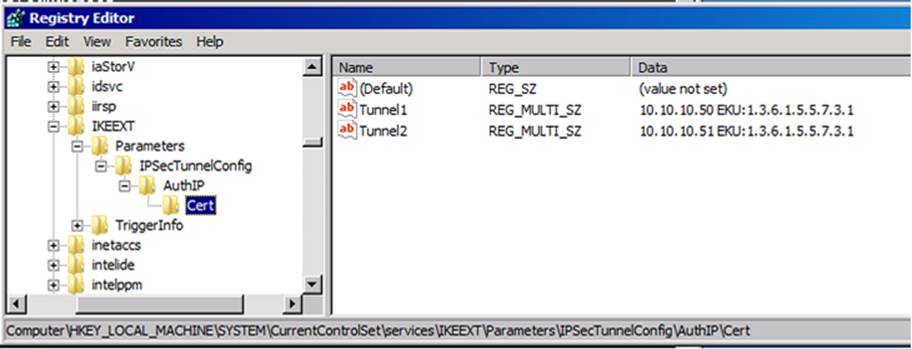
4.4: Registry settings in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003
The validations will be enabled only when the registry keys are configured.
Note The validations will be forced even if the registry keys have no value or data.
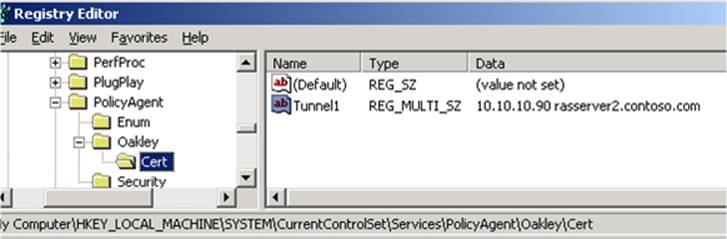
4.4.1: Certification authentication by using Oakley
-
Registry key: HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent\Oakley\Cert
-
Registry name: This can be any name (for example, Tunnel1).
-
Type: REG_MULTI_SZ
-
Data: <IPv4Address> <DNS1> <DNS2> <DNS3> <custom EKU OID>
Data separators can be "space" or "tab" or "new line." For example, the data can also be configured as follows:
Data: <IPv4Address><DNS1>
<DNS2>
<DNS3>
<custom EKU OID>
The custom EKU OID should be configured by using the "EKU:" prefix format as shown in the following:EKU:<EKU OID>
The registry can have more than one registry name:
-
Registry name: This can be any name (for example, Tunnel2).
-
Type: REG_MULTI_SZ
-
Data: <IPv4Address> <DNS4> <DNS5> <DNS6> <custom EKU OID>
The IP address is the address of the tunnel destination and should be the first string in the entry.
Each entry can have no more than 10 DNS names and only one custom EKU specified.
The maximum number of DNS names configured per entry is 10.
Note If the size of the entry exceeds 16,384 characters, that entry will be ignored. This includes the IP address size and EKU size.
Only one EKU can be considered per a tunnel destination (for example, per IP). The search is iterative. If there are more than one "IP" entries configured, the first configured EKU for that IP address entry will be considered for validation.
The maximum number of tunnels that can be configured under the registry path is 1,024.
Notes
-
"IP" values must be configured. Administrators can configure either DNS or EKU based on their needs.
-
If only EKU is configured, we validate the EKU present in the peer certificate and allow for or disallow authentication based on the validation result.
-
If only DNS name is configured, we validate only the subjectAltName present in the certificate and allow for or disallow authentication based on the validation result.
-
If both are configured, we validate only EKU and allow for or disallow authentication based on the validation.
DNS approach:
-
You can specify any string in the Name field.
-
If your server has an IPv6 address, you can specify the same IPv6 address instead of the IPv4 address.
EKU approach: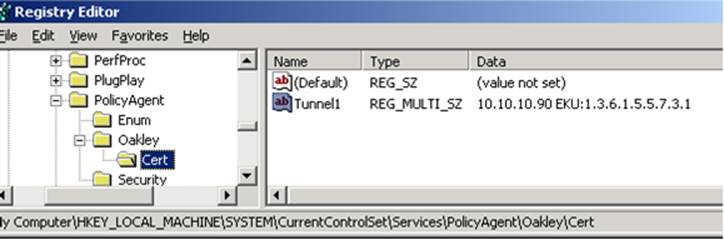
4.5: Windows 8 and Windows 8.1
Validations will be enabled only if the registry key is configured. Be aware that the checks will be enforced by just adding the key even without any registry values or data.
4.5.1: KerbProxy authentication by using AuthIP:
-
Registry key: HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\IKEEXT\Parameters\IPsecTunnelConfig\AuthIP\kerberos
-
Registry name: This can be any string (for example, Tunnel1).
-
Type: REG_MULTI_SZ
-
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address> <SPN1> <SPN2> <SPN3>
Data separators can be "space" or "tab" or "new line." For example, the data can also be configured as follows:
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address><SPN1>
<SPN2>
<SPN3>
The registry can have more than one registry name:
-
Registry name: This can be any string (for example, Tunnel2).
-
Type: REG_MULTI_SZ
-
Data: <IPv4Address or IPv6Address> <SPN4> <SPN5> <SPN6>
The IP address is the address of the tunnel destination and should be the first string in the entry.
The maximum number of SPNs configured per entry is 10.
Note If the size of the entry (including the IP address size) exceeds 16,384 characters, that entry will be ignored. The maximum number of tunnels that can be configured under the registry path is 1,024.
SPN approach:
-
You can specify any string in the Name field.
-
If your server has an IPv6 address, you can specify the same IPv6 address instead of the IPv4 address.

5: Troubleshooting
If IPsec connection failures occur, follow these steps to troubleshoot the issue:
-
Make sure that the correct configuration is performed as described in the earlier sections.
-
Examine the event logs to determine whether the failure is thrown at the initiator or the responder.
-
In Windows 8 and later versions, there are no changes on the responder side. So, the failure can only be from the initiator. If a failure occurs, IKE traces will show a message that resembles the following in the log:
AuthIP peer SPN did NOT match configured SPN
-
In Windows 7 and earlier versions, the failure can be generated from the initiator or the responder.
If there are initiator-side failures, the following events are logged.
|
Failure case |
Initiator |
Responder |
|---|---|---|
|
IKEv1 |
An IPsec main mode negotiation failed. |
An IPsec main mode security association was established. Extended mode was not enabled. A certificate was used for authentication. |
|
An IPsec main mode security association ended. |
||
|
AuthIP |
An IPsec main mode negotiation failed. |
An IPsec main mode negotiation failed. |
If there are responder-side failures, the following events are logged:
|
Failure case |
Initiator |
Responder |
|---|---|---|
|
IKEv1 |
An IPsec main mode security association was established. Extended mode was not enabled. A certificate was used for authentication |
An IPsec main mode security association was established. Extended mode was not enabled. A certificate was used for authentication. |
|
An IPsec quick mode negotiation failed. |
An IPsec main mode security association ended. |
|
|
An IPsec main mode security association ended. |
An IPsec quick mode negotiation failed. |
|
|
AuthIP |
An IPsec main mode negotiation failed. |
An IPsec extended mode negotiation failed. The corresponding main mode security association has been deleted. |
|
An IPsec extended mode negotiation failed. The corresponding main mode security association has been deleted. |
IKE traces
-
Enable the IKE tracing, and reproduce the issue.
-
Stop the IKE tracing.
-
Share the Ikeext.etl file from C:\windows\system32 to the Microsoft support team.
If there are failures, IKE traces will display the following logs.
Failure because of EKU:
-
Peer certificate custom EKU did NOT match with configured EKU for AUTHIP
-
Peer certificate custom EKU did NOT match with configured EKU for IKE
Failure because of Cert:
-
IKE peer certificate DNS Name did NOT matched with configured DNS names
-
AUTHIP peer certificate DNS Name did NOT match with configured DNS names
Windows XP and Windows Server 2003
Oakley logs help identify the cause of IPsec-related failures.
To enable IPsec logging, at a command prompt, type the following command, and then press Enter:
Netsh IPsec dynamic set config ikelogging 1Then, to reproduce the failure case, type the following command:
Netsh IPsec dynamic set config ikelogging 0The Oakley log is generated in the following folder:
C:\winodws\DebugIf there are failures, IKE traces will display the following logs.
Failure because of EKU:
-
Peer certificate custom EKU did NOT matched with configured EKU for IKEv1
Failure because of Cert:
-
Peer certificate DNS Name did NOT match with configured DNS name for IKEv1
Note In the message information listed here, "did NOT matched" is a typographic error that appears in the code.
References
For more information about IPsec, go to the following Microsoft webpage:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831416For more information about CA, see the Advanced Deployment Guide webpage:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831436For more information about how to deploy a single remote access server, go to the following Microsoft Basic Remote Access deployment webpage:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831520For more information about site-to-site VPN, go to the following Microsoft Test Lab Guide webpage:
FILE INFORMATION
The English (United States) version of this software update installs files that have the attributes that are listed in the following tables. The dates and times for these files are listed in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The dates and times for these files on your local computer are displayed in your local time and with your current daylight saving time (DST) bias. Additionally, the dates and times may change when you perform certain operations on the files.
-
The files that apply to a specific milestone (SPn) and service branch (QFE, GDR) are noted in the "SP requirement" and "Service branch" columns.
-
GDR service branches contain only those fixes that are widely released to address widespread, critical issues. QFE service branches contain hotfixes in addition to widely released fixes.
-
In addition to the files that are listed in these tables, this software update also installs an associated security catalog file (KBnumber.cat) that is signed with a Microsoft digital signature.
For all supported x86-based versions of Windows XP
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Oakley.dll |
5.1.2600.6462 |
278,528 |
12-Oct-2013 |
15:56 |
x86 |
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP Professional x64 edition
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
SP requirement |
Service branch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Oakley.dll |
5.2.3790.5238 |
407,040 |
13-Oct-2013 |
05:37 |
x64 |
SP2 |
SP2QFE |
|
Woakley.dll |
5.2.3790.5238 |
361,472 |
13-Oct-2013 |
05:37 |
x86 |
SP2 |
SP2QFE\WOW |
For all supported x86-based versions of Windows Server 2003
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Oakley.dll |
5.2.3790.5238 |
361,472 |
12-Oct-2013 |
15:57 |
x86 |
For all supported IA-64-based versions of Windows Server 2003
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
SP requirement |
Service branch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Oakley.dll |
5.2.3790.5238 |
565,760 |
13-Oct-2013 |
05:37 |
IA-64 |
SP2 |
SP2QFE |
|
Woakley.dll |
5.2.3790.5238 |
361,472 |
13-Oct-2013 |
05:37 |
x86 |
SP2 |
SP2QFE\WOW |
-
The files that apply to a specific product, milestone (SPn), and service branch (LDR, GDR) can be identified by examining the file version numbers as shown in the following table:
Version
Product
Milestone
Service branch
6.0.6002. 18xxx
Windows Vista SP2 and Windows Server 2008 SP2
SP2
GDR
6.0.6002. 23xxx
Windows Vista SP2 and Windows Server 2008 SP2
SP2
LDR
-
GDR service branches contain only those fixes that are widely released to address widespread, critical issues. LDR service branches contain hotfixes in addition to widely released fixes.
Note The MANIFEST files (.manifest) and MUM files (.mum) that are installed are not listed.
For all supported x86-based versions of Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.0.6002.18005 |
334,848 |
11-Apr-2009 |
06:28 |
x86 |
|
Fwpkclnt.sys |
6.0.6002.18005 |
99,816 |
11-Apr-2009 |
06:32 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.18960 |
596,480 |
11-Oct-2013 |
02:07 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.0.6002.18960 |
444,928 |
11-Oct-2013 |
02:08 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
05-Jan-2008 |
11:29 |
Not applicable |
|
Wfp.tmf |
Not applicable |
218,228 |
11-Oct-2013 |
00:39 |
Not applicable |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
334,848 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:52 |
x86 |
|
Fwpkclnt.sys |
6.0.6002.23243 |
98,240 |
12-Oct-2013 |
03:24 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
596,480 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:53 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
446,464 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:53 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
09-Sep-2011 |
11:41 |
Not applicable |
|
Wfp.tmf |
Not applicable |
218,580 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:42 |
Not applicable |
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.0.6002.18005 |
458,240 |
11-Apr-2009 |
07:11 |
x64 |
|
Fwpkclnt.sys |
6.0.6002.18005 |
166,888 |
11-Apr-2009 |
07:15 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.18960 |
781,824 |
11-Oct-2013 |
04:23 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.0.6002.18960 |
462,848 |
11-Oct-2013 |
04:23 |
x64 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
05-Jan-2008 |
11:29 |
Not applicable |
|
Wfp.tmf |
Not applicable |
217,074 |
11-Oct-2013 |
02:29 |
Not applicable |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
458,240 |
12-Oct-2013 |
03:19 |
x64 |
|
Fwpkclnt.sys |
6.0.6002.23243 |
165,312 |
12-Oct-2013 |
03:51 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
781,824 |
12-Oct-2013 |
03:20 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
464,384 |
12-Oct-2013 |
03:20 |
x64 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
15-Nov-2011 |
15:19 |
Not applicable |
|
Wfp.tmf |
Not applicable |
217,466 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:11 |
Not applicable |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.18960 |
596,480 |
11-Oct-2013 |
02:07 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
26-Sep-2013 |
12:46 |
Not applicable |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
596,480 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:53 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
09-Sep-2011 |
11:41 |
Not applicable |
For all supported IA-64-based versions of Windows Server 2008
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.0.6002.18005 |
781,312 |
11-Apr-2009 |
06:59 |
IA-64 |
|
Fwpkclnt.sys |
6.0.6002.18005 |
262,632 |
11-Apr-2009 |
07:03 |
IA-64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.18960 |
1,124,352 |
11-Oct-2013 |
03:43 |
IA-64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.0.6002.18960 |
944,128 |
11-Oct-2013 |
03:43 |
IA-64 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
03-Jan-2008 |
18:54 |
Not applicable |
|
Wfp.tmf |
Not applicable |
217,254 |
11-Oct-2013 |
02:05 |
Not applicable |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
781,312 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:17 |
IA-64 |
|
Fwpkclnt.sys |
6.0.6002.23243 |
261,056 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:52 |
IA-64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
1,124,352 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:18 |
IA-64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
946,688 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:18 |
IA-64 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
15-Mar-2011 |
05:52 |
Not applicable |
|
Wfp.tmf |
Not applicable |
217,516 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:24 |
Not applicable |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.18960 |
596,480 |
11-Oct-2013 |
02:07 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
26-Sep-2013 |
12:46 |
Not applicable |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.0.6002.23243 |
596,480 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:53 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
814 |
09-Sep-2011 |
11:41 |
Not applicable |
-
The files that apply to a specific product, milestone (RTM, SPn), and service branch (LDR, GDR) can be identified by examining the file version numbers as shown in the following table:
Version
Product
Milestone
Service branch
6.1.7601. 18xxx
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
SP1
GDR
6.1.7601. 22xxx
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
SP1
LDR
-
GDR service branches contain only those fixes that are widely released to address widespread, critical issues. LDR service branches contain hotfixes in addition to widely released fixes.
Note The MANIFEST files (.manifest) and MUM files (.mum) that are installed are not listed.
For all supported x86-based versions of Windows 7
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.1.7601.17514 |
494,592 |
20-Nov-2010 |
12:18 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
216,576 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:01 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
679,424 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:01 |
x86 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,028 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:33 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
656,896 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:03 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
10-Jun-2009 |
21:32 |
Not applicable |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
496,128 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:55 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
216,576 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:56 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
681,472 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:56 |
x86 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,028 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:21 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
657,920 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:57 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
10-Jun-2009 |
21:32 |
Not applicable |
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.1.7601.17514 |
705,024 |
20-Nov-2010 |
13:25 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
324,096 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:29 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
859,648 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:29 |
x64 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,028 |
12-Oct-2013 |
03:06 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
830,464 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:30 |
x64 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:51 |
Not applicable |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
706,560 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:23 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
324,096 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:24 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
861,184 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:24 |
x64 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,028 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:49 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
832,000 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:25 |
x64 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:51 |
Not applicable |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
216,576 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:01 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
656,896 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:03 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
04-Jul-2013 |
12:21 |
Not applicable |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
216,576 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:56 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
657,920 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:57 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
09-Jul-2013 |
06:28 |
Not applicable |
For all supported IA-64-based versions of Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.1.7601.17514 |
1,071,616 |
20-Nov-2010 |
10:24 |
IA-64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
566,272 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:34 |
IA-64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
1,500,160 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:34 |
IA-64 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,028 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:59 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
1,112,064 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:36 |
IA-64 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:57 |
Not applicable |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
1,074,176 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:24 |
IA-64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
566,272 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:24 |
IA-64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
1,503,744 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:24 |
IA-64 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,028 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:44 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
1,113,600 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:25 |
IA-64 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:57 |
Not applicable |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
216,576 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:01 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.18283 |
656,896 |
12-Oct-2013 |
02:03 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
04-Jul-2013 |
12:21 |
Not applicable |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
216,576 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:56 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.1.7601.22479 |
657,920 |
12-Oct-2013 |
01:57 |
x86 |
|
Wfp.mof |
Not applicable |
822 |
09-Jul-2013 |
06:28 |
Not applicable |
-
The files that apply to a specific product, milestone (RTM,SPn), and service branch (LDR, GDR) can be identified by examining the file version numbers as shown in the following table:
Version
Product
Milestone
Service branch
6.2.920 0.16 xxx
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
RTM
GDR
6.2.920 0.20 xxx
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
RTM
LDR
-
GDR service branches contain only those fixes that are widely released to address widespread, critical issues. LDR service branches contain hotfixes in addition to widely released fixes.
Note The MANIFEST files (.manifest) and MUM files (.mum) that are installed are not listed.
For all supported x86-based versions of Windows 8
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.2.9200.16734 |
473,600 |
10-Oct-2013 |
09:28 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
245,248 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:10 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.2.9200.16734 |
683,520 |
10-Oct-2013 |
09:29 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
702,464 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:10 |
x86 |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
473,600 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:30 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.20569 |
245,248 |
27-Nov-2012 |
04:22 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
683,520 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:30 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
702,464 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:30 |
x86 |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.2.9200.16734 |
473,600 |
10-Oct-2013 |
09:28 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
245,248 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:10 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.2.9200.16734 |
683,520 |
10-Oct-2013 |
09:29 |
x86 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
2,920 |
10-Oct-2013 |
10:06 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
702,464 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:10 |
x86 |
|
Wfplwfs.sys |
6.2.9200.16734 |
38,744 |
10-Oct-2013 |
10:07 |
x86 |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
473,600 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:30 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.20569 |
245,248 |
27-Nov-2012 |
04:22 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
683,520 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:30 |
x86 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
2,920 |
10-Oct-2013 |
23:31 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
702,464 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:30 |
x86 |
|
Wfplwfs.sys |
6.2.9200.20842 |
38,744 |
10-Oct-2013 |
23:37 |
x86 |
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.2.9200.16734 |
723,968 |
10-Oct-2013 |
09:20 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
381,952 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:15 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.2.9200.16734 |
1,160,192 |
10-Oct-2013 |
09:21 |
x64 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
888,832 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:16 |
x64 |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
718,848 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:26 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.20569 |
378,880 |
27-Nov-2012 |
04:25 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
1,074,688 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:26 |
x64 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
888,832 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:26 |
x64 |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.2.9200.16734 |
723,968 |
10-Oct-2013 |
09:20 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
381,952 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:15 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.2.9200.16734 |
1,160,192 |
10-Oct-2013 |
09:21 |
x64 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
2,920 |
10-Oct-2013 |
11:50 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
888,832 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:16 |
x64 |
|
Wfplwfs.sys |
6.2.9200.16734 |
96,600 |
10-Oct-2013 |
11:53 |
x64 |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
718,848 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:26 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.20569 |
378,880 |
27-Nov-2012 |
04:25 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
1,074,688 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:26 |
x64 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
2,920 |
11-Oct-2013 |
00:50 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
888,832 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:26 |
x64 |
|
Wfplwfs.sys |
6.2.9200.20842 |
96,600 |
11-Oct-2013 |
00:54 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
245,248 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:10 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.16634 |
702,464 |
10-Jun-2013 |
19:10 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.2.9200.20569 |
245,248 |
27-Nov-2012 |
04:22 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.2.9200.20846 |
702,464 |
10-Oct-2013 |
22:30 |
x86 |
For all supported x86-based versions of Windows 8.1
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.3.9600.16427 |
549,888 |
12-Oct-2013 |
21:14 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
264,192 |
22-Aug-2013 |
02:40 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.3.9600.16427 |
730,112 |
12-Oct-2013 |
21:02 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
566,784 |
22-Aug-2013 |
02:19 |
x86 |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.3.9600.16427 |
549,888 |
12-Oct-2013 |
21:14 |
x86 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
264,192 |
22-Aug-2013 |
02:40 |
x86 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.3.9600.16427 |
730,112 |
12-Oct-2013 |
21:02 |
x86 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,059 |
13-Oct-2013 |
00:27 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
566,784 |
22-Aug-2013 |
02:19 |
x86 |
|
Wfplwfs.sys |
6.3.9600.16427 |
69,464 |
13-Oct-2013 |
00:45 |
x86 |
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bfe.dll |
6.3.9600.16427 |
828,416 |
12-Oct-2013 |
21:48 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
411,136 |
22-Aug-2013 |
09:43 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.3.9600.16427 |
1,104,384 |
12-Oct-2013 |
21:34 |
x64 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
716,800 |
22-Aug-2013 |
09:11 |
x64 |
|
Bfe.dll |
6.3.9600.16427 |
828,416 |
12-Oct-2013 |
21:48 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
411,136 |
22-Aug-2013 |
09:43 |
x64 |
|
Ikeext.dll |
6.3.9600.16427 |
1,104,384 |
12-Oct-2013 |
21:34 |
x64 |
|
Networksecurity-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,059 |
13-Oct-2013 |
02:41 |
Not applicable |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
716,800 |
22-Aug-2013 |
09:11 |
x64 |
|
Wfplwfs.sys |
6.3.9600.16427 |
136,536 |
13-Oct-2013 |
02:48 |
x64 |
|
Fwpuclnt.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
264,192 |
22-Aug-2013 |
02:40 |
x86 |
|
Nshwfp.dll |
6.3.9600.16384 |
566,784 |
22-Aug-2013 |
02:19 |
x86 |
|
File name |
SHA1 hash |
SHA256 hash |
|---|---|---|
|
Windows6.0-KB2862152-ia64.msu |
80EE12A2E51477C621392A0665BC837CFF8FC29B |
55D9566C4062721EA0B8C9B02B2DE1FC5A48B6216338012BA7C3E15C9F78EC4A |
|
Windows6.0-KB2862152-x64.msu |
E24C86C21DDD00ADA6B49EE1C2A037F9D2CBD8EF |
5C2D595720F98D351400593A562DBD5812AAAADE31E7B92E8B2493771AF8EDD3 |
|
Windows6.0-KB2862152-x86.msu |
C062CCF8CCCB24411D223934451EB25323C5B9BC |
1EE3C6408CC3EE8CACA8CA0C9A23089AE8F4461FFB277414F9EFC0E61B2A30B5 |
|
Windows6.1-KB2862152-ia64.msu |
61E5FC414F88C1B15FB27AB905AB67652B188FF2 |
C76E6DBBF345D2CA602AA4DCA83C780A7DF12D13F7570FDF57A605D81C33173F |
|
Windows6.1-KB2862152-x64.msu |
72BBAF8697440A998DF17DB09A69B24D96C4FE07 |
7764527EA105A36339EAF0DD09B45DE8EEB3EF68B4E09B69104FD63040C97365 |
|
Windows6.1-KB2862152-x86.msu |
EAC008F3D7E22B10E646D969656C48C25FADC6B4 |
64E90C46DC94A68DC5B2DA9AEB426EB07E660F5D32AB85A6111103F15E115F47 |
|
Windows8-RT-KB2862152-x64.msu |
717A29A94CFCCE8F663E555075CDE12E2A7A836D |
A1EC074D8B1576CC3F7E5847451EA13E9D189ABFF1B0C05100522C579580345E |
|
Windows8-RT-KB2862152-x86.msu |
B762EE6FDB2CE341546C3A93C919CD5A482A99A9 |
CC2B0CEFEEFAAEC76966530C38B88281F4DEE46223DE7348E2C258DAB06E6C2E |
|
Windows8.1-KB2862152-x64.msu |
EC8DF98AE6D52A827266403A267F708A9CDE9B38 |
26068674EFEE40DA6B682429FD8876DE75405A83FE3A3689711884188FB3B3AE |
|
Windows8.1-KB2862152-x86.msu |
63D555F539C3D80AF8C4CE23179A9DE447810502 |
0FB82BB48506DE4883E4DCF518E7745AEBF56B47DD9F314563B7B8EA49B24155 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-ia64-DEU.exe |
5BD38A43C1E04B8CDF94DF9F4B7C58F6B93B4C27 |
4004B7BACEFF854FD4E8FD72B7BCD5A07AD29A3B3979CAF738C41117487B557D |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-ia64-ENU.exe |
CC67EC663C2C933B2781436EA37F6BE2AEADD4C1 |
86A30C9F2DB197C099EE5BDB95CA7B7121D87D94A8AB3ADEAEAB64E099BAD7C9 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-ia64-FRA.exe |
FD8AF00F493485D70C94E1113DB955F2F6774444 |
58E4A5925C0A400BC3FCA664DC0E60FC930FFB54CD7879D4E0620A5DC3ADD996 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-ia64-JPN.exe |
BC417216D77EABAED92C54C1828C09A8F1EE266A |
7122AF3D47607C5A6E7BADB8A0A740714FB908975074C7D64B6E0F9C23CA6141 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-CHS.exe |
7E8BBBA255E7DC0BE62AE188A40A8F004FCB5E4F |
4DFA6A4E6CF86DC4BA1EA0F10204F8275EB61F28B2BF5D5AC58F314760614272 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-CHT.exe |
C3707B843C2914F02FF728691B7489460557328B |
7B4829AE8CA47CF789FC3C084291B30D99D24497C5223AAD2968DCE0E7A2A214 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-CSY.exe |
17B5A8D82581E04B3DC8359A55A0775E53BAF1A6 |
5049340582FB9E145B2B3104B1066984AEBB1EE352064F1D7C9C6BDA073D2097 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-DEU.exe |
A75DC6744A60D8CADB39D1D9963FAC7B608CAA89 |
982A7F6DF2067AA891E6890D0119CD1D5CA2FCB6238CF341D47293B80B7A3EBA |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-ENU.exe |
8D96F688B35EFA32EEC1B05C92A8422D304E972D |
5192DD6E6C38C635AFF68A926C60FFF1FDC1433982E5C0FFFAEE5C3EDD9C6F2C |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-ESN.exe |
37DCEF5107C1C157B738FED12CAC921100EEFF6F |
63D2CDD7D92FEAD9F72D0BEC29B5B4B25626B814BAEF517AF3B9B9252993B1E2 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-FRA.exe |
60BB2ECB93869D41E432901ADB1D3ED4B71CD700 |
0E37AB5EE438261F8B2B623180BE12B05AD13ECA4F7D246D6EBC90110E2EF179 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-HUN.exe |
0EEEB1F90C9BBDBC12368029DD5DCBC94A9499E8 |
ACE72D7C2CF26E99044BF7B19CBBC25067BAA7B5972C656C1AB0256DD43B877E |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-ITA.exe |
DC2AB04A66B46AA9F97B817924007E9FCD5EB306 |
F032AE531AF7C4B9B03DB92F4470D37E4F9A078EFAEE7DB8C2DE7C3AEB54A7F5 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-JPN.exe |
1FBBBEC7AB9B764D439213E5ACD7278F6114792F |
42F8DB54F37DD659221168226CDBADE0F1614FB7FF06DB3C037667EF4661DDB8 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-KOR.exe |
B7CBCEA8AFCE0A77273B5264B0E90EE57BEA8423 |
E24C14DB1809D6E7A9AE7D2BF52E84B591B7332D3F073D6272CACF2434573ADB |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-NLD.exe |
799BE730609FE5D4CDB56F46A1F4520F50183A9E |
4FD53C68F54668FE0CCE9F51DA1EFFF36E6050C5CBBD42E94C3453C036C54BAF |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-PLK.exe |
B5160A3964D9DD776E6DD659B47593270FA4D79D |
4E5C3C8B9859BFA8F83CBA2D7042A956CA8A69AFFF123E09899D16312FCA6D12 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-PTB.exe |
83CCFE642630C0054105D0441FEA09204DEA86CE |
4156FF7C97627C42A95871F1D8666ECF36C6146A38804BE71C2C93EF082052DE |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-PTG.exe |
B7D66DB2EF501D9DF68ECE685D095EABE4CDE276 |
8E88E57841BF640E5382E0808DEEA5F9FCFBD91CC0C502D071969A6BCAE4C7FB |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-RUS.exe |
B982BCC1C5D1C0AF677940555429223C7D134E7D |
E7D524899F14DD4739C48056468D66C8C59DBD6BF629942060AECF3397307F72 |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-SVE.exe |
4EF34DE5D662004089E77A23F162A47359E5BFFA |
6C779C1F31C7B2587D4B097998B1C28D63FDAB19DF5AF9E6263A1F49E15FBFFE |
|
WindowsServer2003-KB2862152-x86-TRK.exe |
5506F386C876A0BDB71D722BE785CC9C4B6DBB48 |
8443ADF3249DBD3C8A1C0939B4DFC717EE94B9DD609CAAD40317992EA33E6006 |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-CHS.exe |
D15894E4D38D740F1F6D40EF14D1E2CB663D3740 |
9AD8CA4C5AD11E261E1726009182FF9D256FF37C17F5CA296AFE28859D5B6E5E |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-CHT.exe |
E69F9455BA88CCF1F579118C0DA787A3AB66DE43 |
47FB6E9D05D63C7984E745B7709E11E27D595BA385FF667EB31DD5922F9581AA |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-DEU.exe |
E6F17C263EB3824534D3A23187C51382393A9111 |
A09D50A344E7ECF3010C0B5530EB36C74FCE039985E9950A67FA1B971B31E5A0 |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-ENU.exe |
D97C7E8E60E51CEB4C10F40CD0163DFCC0FA0E13 |
13BCFE30002F3AD0280D14287B22FBF830297EF839A93C6E539EBB19814073F5 |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-ESN.exe |
EEA452A980769A5B00D163EE7390B11579345E4A |
EF97F201F03D7CA58FF4B9C84B1F301DBAA750EA39BD55207BD3F2A7F97258DD |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-FRA.exe |
6E6B16D63B5CA7D55CE90A4569EF9BB486FBE2E8 |
5F44490CA1A9349C879E8BFC0CF01A7BAC0A296125ED9762FAACF0218F84CEEE |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-ITA.exe |
4C0A6CF4A7B836918B139EA4947702CDB203F29C |
91CE056ACFF2C1022BFCD7A52850EF1C2341718207BDBAD8FEDEDAB17A48978D |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-JPN.exe |
F3CD39130480F41AB23B09848A4A75BE1598B9F2 |
D8FEECC1A21175819FF43C008A9CC2111E94CBE5B2D7D20C82645AFAEC10FA39 |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-KOR.exe |
6AF20E71CF92A1D968E4D59894FFF9BF267361FB |
220642EFC5483967286C554D6E39B3929650100ED0C6AAC3BB0F69739129F950 |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-PTB.exe |
CBB061A4942A123BC69DA4AA57F5D0AB1B49E365 |
C502413E7680C55E82F2D9A7D1B8EA8958D7967A758FFABD18C38806BA271360 |
|
WindowsServer2003.WindowsXP-KB2862152-x64-RUS.exe |
E0FA5FB8342E2ED7C74762ED70AC69744BB77ED8 |
9F2A281001193FEFE1F70B776E62553971CCBB1219B605800526C48AB66955CF |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-ARA.exe |
08C5CAA13FC12FF96BE70EB407EDB46E53631B02 |
8D0826034D9A7B390BF54E25A0F54CB7C29A9335C201FD5F7334899B5E159048 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-CHS.exe |
44115DD4A313FE9FE60C718F9C5EA351B134810E |
B93335E701871D7308B212556AE62CA68164931662CAAEEBA3F6FA8A2FC1792D |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-CHT.exe |
2C50E771B0E2AFC7970BF6C50122C3C52563F79C |
D27B6B2A20FF1273BB4A145B69F88A4AC57E6118D2DF5C0068ECF348840808FB |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-CSY.exe |
BD3DF5F3DD9711701926652FCBBB8F7BCEECC20B |
311FFDB7C7FDD1BD9A9A4347F29B2ED4322248F9938C48598E175E1B2E932DEF |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-DAN.exe |
D862174B345C67E95F9A8BE9E32B0EE42375231D |
7687F536680D58036F3A154C695C0DADE51A1A459757005397B0B2C08E2B1A6B |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-DEU.exe |
EC84928C2543F65D5EFB65FECF26C714AA85CF4F |
E884909D9E9B884E364BD3EACC7C93436FF586398C43D0F7E0E457D140C737FB |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-ELL.exe |
53F4E15D7E65B9973DF6C95F1BEFD95579EEAF09 |
C467E34B2F5FACB6C3B81CBDF63036DCB53933162193F6F32F0D2D0A8F4831F8 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-ENU.exe |
0457906284FF7FD706D77A69AC337CE7F65C7919 |
0CC60947AFACBA9D8DF0BB3E7D6A6FA4E51C67AFCAE87082E2956B1534E05F9E |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-ESN.exe |
6FC07F443C1C20F9DBABBDEF941FE7EA867493CA |
092BD98A6D86FCBD5B2F80C9533B54B1EBC07A6752A1D8751369BA410FB52ED6 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-FIN.exe |
547B01212FBC27DEE724EC2DC38DE50F919094A1 |
23620EFC04CF1695E9E3C9B0F8E023A22053088386EF49186F98156171861D43 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-FRA.exe |
D0F53AAD13B2B0A79762801D134E7E40D805F105 |
38718267E7C8090E8C407B2E68F3F6CA7205FCC8246F521E653DA9884512909D |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-HEB.exe |
8E965464A33CBF7FDD07B152E39843445B5D9B37 |
ADDC0E3FD19E02559EE684339B0CFDF61F74B812CC7A8DE22360779BB36D9E6C |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-HUN.exe |
5600AE08B7CEA40FB83416784E2F39D2C0912D32 |
5590CA39913D20F9F66A364A8CAF55B1627BCFCE84019A471457AAE7243519CE |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-ITA.exe |
0320BED1B72A0A93A60323CDF19018190CE6C852 |
103B7DF4D26767943618099A21D1C28E713E51A41F46CD8A6471A21B67FAC58F |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-JPN.exe |
E5BFF9F5D16658B02BB69C1B967A3C232604B02F |
6F21CFDFA9EE500970B8712F441682C8539074E7DB85493233448D105B0B1B85 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-KOR.exe |
A30EC90A5C4E9A28FB91505EB50426F0411AD788 |
E44D2458F5899BCC6E992C05AC9F3E25E508A6C9408C0B90723FE6DFCB0F0DC1 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-NLD.exe |
9C7C9B75979D0DD6653D31743C1B99DCE50D3FB7 |
4008D539CCB0CFDC7503E5FB1D38BFABCF7ECAE7C1ED1C65926ECE19E3B8A581 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-NOR.exe |
B2C79C2E9A3D4AEC07AC0CA95990109AB23546F0 |
080BE1727CE5D3BDF3D96A20D4D961959E4FB0D2BB82FF3F99DEAB920CCDD42C |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-PLK.exe |
337C1A1BA95EDBF09E9406BE80748D1DB80346CF |
C54AD936F9051AABA23906BF9D04EDAE32F3CAB3B2A57EA75B44E12A95500C89 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-PTB.exe |
4C3F4AD1510F0373F0F4E6B73CDDAE9B66392CAB |
C30CA0116215D36D540A4062AFA7C7F45EA956F77CB6B9CA109D2B96628B338C |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-PTG.exe |
5927992A54D4AF2429C755CED1050D2447CD15EA |
8AF1670ED2B30CFD201CD250DED392ED7375FD8EB4916F6FAD5CB0BD7A09F38B |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-RUS.exe |
69CCC88DDA04A5EAB488D651EFD0FE2BF1C3DE1E |
AAAABC926CECD40D5866207181BAF6BFF7D3D17D51DE8E2B4EDCFD334599F11B |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-SVE.exe |
ECAE50464CC4E4711D69DBFCA79FA50CC3C14D27 |
6067587091E45118B8A480C1BC202EB1D4D61FD740B19D381101136F129201E7 |
|
WindowsXP-KB2862152-x86-TRK.exe |
1F11C641C93BF5073C3DA66C03FEC93CAEF3A171 |
7DB972F5221D697263B0DE5CE8A1748D4E9F9B2591951C9A943EDC669B422190 |










