A histogram is a column chart that shows frequency data.
Note: This topic only talks about creating a histogram. For information on Pareto (sorted histogram) charts, see Create a Pareto chart.
Excel
-
Select your data.
(This is a typical example of data for a histogram.)
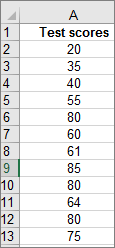
-
Click Insert > Insert Statistic Chart > Histogram.
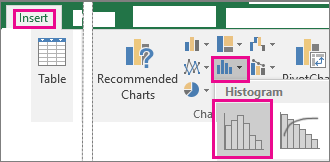
You can also create a histogram from the All Charts tab in Recommended Charts.
Tips:
-
Use the Design and Format tabs to customize the look of your chart.
-
If you don't see these tabs, click anywhere in the histogram to add the Chart Tools to the ribbon.

-
Right-click the horizontal axis of the chart, click Format Axis, and then click Axis Options.
-
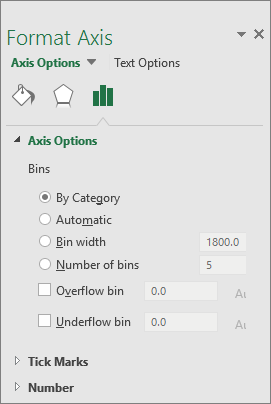
Use the information in the following table to decide which options you want to set in the Format Axis task pane.
Option
Description
By Category
Choose this option when the categories (horizontal axis) are text-based instead of numerical. The histogram will group the same categories and sum the values in the value axis.
Tip: To count the number of appearances for text strings, add a column and fill it with the value “1”, then plot the histogram and set the bins to By Category.
Automatic
This is the default setting for histograms. The bin width is calculated using Scott’s normal reference rule.
Bin width
Enter a positive decimal number for the number of data points in each range.
Number of bins
Enter the number of bins for the histogram (including the overflow and underflow bins).
Overflow bin
Select this check box to create a bin for all values above the value in the box to the right. To change the value, enter a different decimal number in the box.
Underflow bin
Select this check box to create a bin for all values below or equal to the value in the box to the right. To change the value, enter a different decimal number in the box.
Tip: To read more about the histogram chart and how it helps you visualize statistical data, see this blog post on the histogram, Pareto, and box and whisker chart by the Excel team. You may also be interested learning more about the other new chart types described in this blog post.
Automatic option (Scott’s normal reference rule)
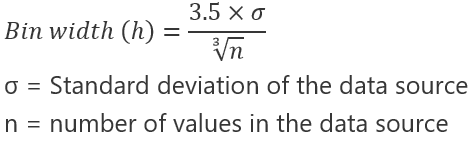
Scott’s normal reference rule tries to minimize the bias in variance of the histogram compared with the data set, while assuming normally distributed data.
Overflow bin option

Underflow bin option

Outlook, PowerPoint, Word
-
Select your data.
(This is a typical example of data for a histogram.)

-
Click Insert > Chart.
-
In the Insert Chart dialog box, under All Charts, click Histogram , and click OK.
Tips:
-
Use the Design and Format tabs on the ribbon to customize the look of your chart.
-
If you don't see these tabs, click anywhere in the histogram to add the Chart Tools to the ribbon.

-
Right-click the horizontal axis of the chart, click Format Axis, and then click Axis Options.

-
Use the information in the following table to decide which options you want to set in the Format Axis task pane.
Option
Description
By Category
Choose this option when the categories (horizontal axis) are text-based instead of numerical. The histogram will group the same categories and sum the values in the value axis.
Tip: To count the number of appearances for text strings, add a column and fill it with the value “1”, then plot the histogram and set the bins to By Category.
Automatic
This is the default setting for histograms.
Bin width
Enter a positive decimal number for the number of data points in each range.
Number of bins
Enter the number of bins for the histogram (including the overflow and underflow bins).
Overflow bin
Select this check box to create a bin for all values above the value in the box to the right. To change the value, enter a different decimal number in the box.
Underflow bin
Select this check box to create a bin for all values below or equal to the value in the box to the right. To change the value, enter a different decimal number in the box.

Follow these steps to create a histogram in Excel for Mac:
-
Select the data.
(This is a typical example of data for a histogram.)

-
On the ribbon, click the Insert tab, then click
Tips:
-
Use the Chart Design and Format tabs to customize the look of your chart.
-
If you don't see the Chart Design and Format tabs, click anywhere in the histogram to add them to the ribbon.
In Excel Online, you can view a histogram (a column chart that shows frequency data), but you can’t create it because it requires the Analysis ToolPak, an Excel add-in that isn’t supported in Excel for the web.
If you have the Excel desktop application, you can use the Edit in Excel button to open Excel on your desktop and create the histogram.
-
Tap to select your data.

-
If you're on a phone, tap the edit icon

-
Tap Insert > Charts > Histogram.
If necessary, you can customize the elements of the chart.
Note: This feature is only available if you have a Microsoft 365 subscription. If you are a Microsoft 365subscriber, make sure you have the latest version of Office.
Buy or try Microsoft 365
-
Tap to select your data.

-
If you're on a phone, tap the edit icon

-
Tap Insert > Charts > Histogram.
To create a histogram in Excel, you provide two types of data — the data that you want to analyze, and the bin numbers that represent the intervals by which you want to measure the frequency. You must organize the data in two columns on the worksheet. These columns must contain the following data:
-
Input data This is the data that you want to analyze by using the Histogram tool.
-
Bin numbers These numbers represent the intervals that you want the Histogram tool to use for measuring the input data in the data analysis.
When you use the Histogram tool, Excel counts the number of data points in each data bin. A data point is included in a particular bin if the number is greater than the lowest bound and equal to or less than the greatest bound for the data bin. If you omit the bin range, Excel creates a set of evenly distributed bins between the minimum and maximum values of the input data.
The output of the histogram analysis is displayed on a new worksheet (or in a new workbook) and shows a histogram table and a column chart that reflects the data in the histogram table.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in Communities.
See Also
Create a sunburst chart in Office










